What is Anatomy and Physiology?
Anatomy:
-Describes the structures of the body
-What they are made of
-Where they are located
-Associated structures
Physiology:
-Is the study of:
-Functions of anatomical structures
-Individual and cooperative functions
KEY CONCEPT:
-All physiological functions are performed by specific anatomical structures
-These functions follow standard physical and mechanical principles
What do anatomists and physiologists do?
Specialties of Anatomy:
-Gross Anatomy, or macroscopic anatomy examines large, visible structures:
-Surface anatomy:
-Exterior features
-Regional anatomy:
-Body areas
-Systemic anatomy:
-Groups of organs working together
-Developmental anatomy:
-From egg (embryology) to maturity
-Clinical anatomy:
-Medical Specialties
-Microscopic anatomy examines cells and molecules:
-Cytology:
-Cells and their structures
-Cyt=cell
-Histology:
-Tissues and their structures
Specialties of Physiology
-Cell physiology
-Processes within and between cells
-Special physiology
-Functions of specific organs
-Systemic physiology:
-Functions of an organ system
-Pathological physiology:
-Effects of diseases
How are living things organized?
From Simple to Complex
-Atoms
-Are the smalled chemical units
-Molecules
-Are a group of atoms working together
-Organelles:
-Are a group of molecules working together
-Cells:
-Are a group of organelles working together
-Tissues:
-Are a group of similar cells working together
-Organs:
Are a group of different tissues working together
-Organ System:
-Are a group of organs working together
-Organism:
-is an individual
Organizing a Muscle
-Protein molecules (chemical level)
-Protein filaments (organelle level)
-Muscle cells (cellular level)
-Cardiac muscle tissue (tissue level)
-Heart (organ level)
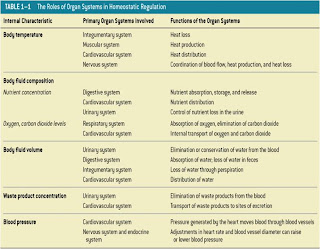
The 11 Organ Systems
KEY CONCEPT:
-The body is divided into 11 organ systems
-All organ systems work together
-Many organs work in more than 1 system
-Homeostasis: All body systems working together to maintain a stable internal environment.
-Systems respond to external and internal changes to functions within a normal range (body temperature, fluid balance)
-Failure to function within a normal range results in disease
Mechanisms of Regulation
-Autoregulation (intrinsic):
-Automatic response in a cell, tissue, or organ
-Extrinsic regulation:
-Responses controlled by nervous and endocrine systems
Maintaining Normal Limits
Maintaining Normal Limits
-Receptor:
-Recieves the stimulus
-Control center:
-Processes the signal and sends instructions
-Effector:
-Carries out instructions
Negative Feedback
-The response of the effector negates the stimulus
Positive Feedback
-The responseof the effector reinforces the stimulus
Working Together
-Systems integration:
-Systems work together to maintain homeostasis
KEY CONCEPT:
-Homeostasis is a state of equilibrium:
-opposing forces are in balance
-Physiological systems work to restore balance
-Failure results in disease or death
What are the anatomical terms used to describe body sections, regions, and relative positions?
Anatomical Landmarks
-Superficial characteristics:
-Surface parts
-Names
-Adjectives
KEY CONCEPT:
-Anatomical position:
-Hands at sides, palms forward
-Supine:
-Lying down, face up
-Prone:
-Lying down, face down
Quadrants and Regions
- 4 abdominopelvic quadrants around umbilicus
-9 abdominopelvic regions
-Internal organs associated with abdominopelvic regions
Which Direction?
-Lateral:
-Side view
-Frontal:
-Front view
-Anatomical Direction:
-Refers to the patient's left or right
3 Dimensions
-A 3 dimensional axis
Section:
-A slice parallel to a plane
What are the major body cavities and their subdivisons?
The Ventral Body Cavity
- Coelom:
-Divided by the diaphragm into the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelivc cavity
Isolating the Organs
-Serous membranes:
-Consist of perietal layer and visceral layer
Dividing the Cavities
-Thoracic Cavity:
-Divided the mediastinum into 2 pleural cavities
SUMMARY:
-Structure and function in anatomy and physiology
-Vocabulary and anatomical terms
-Levels of physical organization
-Homeostasis and feedback
-Systems integration and equilibrium
-Dividing and describing the body
-Locations and functions of major organ systems













Hey! I wanted to use your diagrams of the abdominopelvic regions but I need to site an original source. Can you tell me where you got them from? Thanks!
ReplyDelete